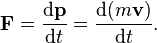SUMMARY
The symbols "d" and "p" in physics represent the derivative and momentum, respectively. The derivative, denoted by "d," is crucial for understanding rates of change, particularly in the context of calculus. Momentum, represented by "p," is defined as the product of mass and velocity, with vectors indicated in bold. A solid grasp of these concepts is essential for comprehending fundamental physics equations, such as the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of calculus, specifically derivatives
- Familiarity with basic physics concepts, including force and acceleration
- Knowledge of vector notation in physics
- Basic understanding of momentum and its formula
NEXT STEPS
- Study calculus focusing on derivatives and their applications in physics
- Explore the concept of momentum and its implications in various physical scenarios
- Learn about Newton's laws of motion and their relationship to force and acceleration
- Review vector mathematics and its role in physics equations
USEFUL FOR
Students beginning their studies in physics, educators teaching introductory physics concepts, and anyone interested in the mathematical foundations of physical laws.