SUMMARY
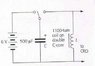
The discussion centers on the function of a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) in monitoring electrical oscillations in a parallel LC circuit, specifically involving a capacitor and an inductor. Participants confirm that the CRO measures voltage oscillations resulting from energy exchange between the capacitor and inductor, with initial conditions of 6V for the capacitor and zero current for the inductor. The resistor's role is debated, with suggestions that it may monitor input current or assist in discharging the capacitor, although it is considered superfluous due to the high output impedance of the signal generator.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of parallel LC circuits and resonance
- Knowledge of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) operation
- Familiarity with energy exchange principles in inductors and capacitors
- Basic electrical circuit analysis skills
NEXT STEPS
- Research the principles of resonance in LC circuits
- Learn about the operation and applications of Cathode Ray Oscilloscopes (CRO)
- Investigate the role of resistors in electrical circuits, particularly in LC circuits
- Explore the effects of component arrangement on circuit behavior, specifically in LC configurations
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, physics students, and hobbyists interested in circuit design and analysis, particularly those working with oscillation circuits and CRO measurements.