SUMMARY
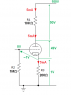
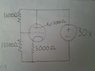
The grid voltage in vacuum tubes is measured with respect to the cathode, not the anode plate. When a vacuum tube data sheet specifies a grid voltage, it indicates the negative voltage required for proper biasing, typically referenced to ground. In practical applications, resistors such as R2 and R3 are used to establish this negative grid voltage, calculated using Ohm's Law. For example, with a 100V power supply and a specified Vg of -1V for a 5mA anode current, the appropriate resistor values can be determined to achieve the desired input impedance.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of vacuum tube operation and biasing techniques
- Familiarity with Ohm's Law and resistor calculations
- Knowledge of circuit diagrams and voltage reference points
- Experience with JFET transistor behavior in relation to grid voltage
NEXT STEPS
- Research vacuum tube biasing methods and their impact on performance
- Learn about the role of grid resistors in tube circuits
- Study the relationship between anode current and grid voltage in vacuum tubes
- Explore JFET transistor characteristics and their similarities to vacuum tube operation
USEFUL FOR
Electronics engineers, hobbyists working with vacuum tubes, and anyone interested in understanding tube circuit design and biasing techniques.