SUMMARY
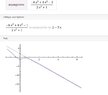
The correct slant asymptote for the function \(\frac{-6x^3 + 4x^2 - 1}{2x^2 + 1}\) is \(y = -3x + 2\). This conclusion is derived from performing polynomial long division, which reveals that the function approaches the linear equation as \(x\) approaches infinity. Although the function never actually reaches the asymptote due to the presence of a non-zero remainder, the asymptote is significant as it describes the end behavior of the function. Understanding this concept clarifies the relationship between polynomial degrees and their asymptotic behavior.
PREREQUISITES
- Polynomial long division
- Understanding of asymptotes in rational functions
- Knowledge of polynomial degrees and their significance
- Graphical interpretation of functions and their limits
NEXT STEPS
- Study polynomial long division techniques in detail
- Learn about horizontal and vertical asymptotes in rational functions
- Explore the concept of limits and end behavior in calculus
- Investigate graphical representations of rational functions
USEFUL FOR
Students of calculus, mathematics educators, and anyone interested in understanding the behavior of rational functions and their asymptotes.