Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the convergence of the sequence defined by \( z_{n+1}=\sqrt{a+z_n} \) for \( a>0 \) and \( z_1 > 0 \). Participants explore the conditions under which the sequence converges, the bounds required for the monotone convergence theorem, and the behavior of the sequence based on initial values.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants note that the sequence is bounded below by \( 0 \), but express uncertainty about establishing an upper bound.
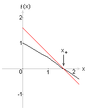
- One participant introduces the concept of fixed points, identifying an attractive fixed point at \( x_{+}= \frac{1+\sqrt{1+4 a}}{2} \) and a repulsive fixed point at \( x_{-}= \frac{1-\sqrt{1+4 a}}{2} \).
- It is proposed that if \( 0x_{+} \), the sequence will be monotonically decreasing.
- Participants suggest proving that if \( z_n < x_{+} \), then \( z_{n+1} < x_{+} \) to establish an upper bound through induction.
- There are discussions about the ratio \( \frac{z_{n+1}}{z_n} \) and how it can be shown to be greater than \( 1 \) under certain conditions, indicating that the sequence is increasing.
- Some participants emphasize the need to consider different cases based on the initial value \( z_1 \) relative to \( x_{+} \).
- One participant expresses a desire to keep the discussion aligned with the book's assumptions, avoiding advanced concepts not yet covered.
- A later reply reiterates the recursive relation and discusses the behavior of the function \( f(x) \) for specific values of \( a \), noting that it has one attractive fixed point.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the need to establish bounds and the behavior of the sequence based on initial conditions, but multiple competing views remain regarding the specific approaches to proving convergence and the implications of different initial values.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight the dependence on the initial value \( z_1 \) and the parameter \( a \) in determining the sequence's behavior, indicating that the analysis may vary significantly based on these factors.