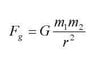Husker70
- 89
- 0
Homework Statement
A satellite of the Earth has a mass of 100kg and is at an altitude of 2.00x10^6m.
(a) What is the potential energy of the satellite-Earth system? (b) What is the magnitude
of the gravitational force exerted by the Earth on the satellite? (c) What force does the
satellite exert on the Earth?
Homework Equations
(a) Ug = - G m1m2/r
Mass of Earth = 5.98x10^24 kg
Radius of Earth = 6.37x10^6 m
The Attempt at a Solution
(a) I took the mass of the Earth times the 100kg satellite/the Altitude plus the radius of earth
Ug = G (5.98x10^24kg)(100kg)/2.00x10^6m(6.37x10^6m)
I'm not sure what the G is for.
Thanks,
Kevin