SUMMARY
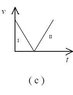
The correct velocity-time graph for a ball thrown straight up is represented by option D. This graph accurately depicts the ball's velocity reaching zero at the apex before falling back down, illustrating the effects of gravity throughout the motion. The discussion highlights the importance of understanding acceleration as a vector, emphasizing that while the ball decelerates on the way up, it accelerates on the way down, confirming that the acceleration due to gravity is consistently negative. Participants debated the merits of options C and D, ultimately concluding that only D correctly represents the ball's motion under the influence of gravity.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic kinematics, specifically velocity and acceleration.
- Familiarity with the concepts of free fall and gravitational acceleration.
- Knowledge of interpreting velocity-time graphs.
- Ability to differentiate between scalar and vector quantities in physics.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of kinematics in one dimension, focusing on velocity and acceleration.
- Learn about the effects of gravity on projectile motion, including the equations of motion.
- Explore the differences between scalar and vector quantities in physics.
- Practice interpreting various types of motion graphs, including position-time and velocity-time graphs.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, educators teaching kinematics, and anyone interested in understanding the motion of objects under the influence of gravity.
 …
…