SUMMARY
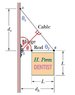
The discussion focuses on determining the relevant angles for calculating torque in a cable system with a hinge as the axis of rotation. The torque equation is defined as Torque = Force * radius, where the radius is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force. Participants emphasize the importance of using the correct angle, either phi or theta, and suggest leveraging similar triangles to compute the necessary dimensions for torque calculations. The conversation highlights the relationship between angles and the geometry of the setup, specifically using right triangles to derive the required values.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of torque and its equation: Torque = Force * radius
- Knowledge of trigonometric functions, particularly sine
- Familiarity with right triangles and the concept of similar triangles
- Basic geometry skills to analyze angles and lengths in diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of torque in mechanical systems
- Learn how to identify and use similar triangles in problem-solving
- Explore trigonometric identities and their applications in physics
- Investigate the role of angles in rotational dynamics
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and rotational dynamics, as well as anyone needing to understand torque calculations in engineering contexts.