AGNuke
Gold Member
- 455
- 9
We have to determine in which of the following options, the first ion is more stable than the second.
1.
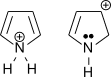
2.
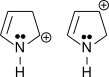
3.
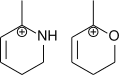
4.

5.
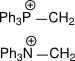
6.
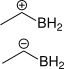
Attempt at the question
1. Since in the first one, +ve charge is due to bonding, not deficiency of electrons.
2. First one can get lone pair from N.
3. N can easily donate its lone pair as opposed to O.
4. O can easily affect the -ve charge density by inductive effect.
5. P can handle +ve on itself more appreciably than N.
6. Backbonding is possible in 2nd case.
The problem is that I have marked 4 options but only 3 options are right as per the answer key. Is it that the answer key is wrong?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Attempt at the question
1. Since in the first one, +ve charge is due to bonding, not deficiency of electrons.
2. First one can get lone pair from N.
3. N can easily donate its lone pair as opposed to O.
4. O can easily affect the -ve charge density by inductive effect.
5. P can handle +ve on itself more appreciably than N.
6. Backbonding is possible in 2nd case.
The problem is that I have marked 4 options but only 3 options are right as per the answer key. Is it that the answer key is wrong?
Last edited:

