- #1
zenterix
- 480
- 70
- Homework Statement
- My question is about concepts of Lewis structures and VSEPR model. I will go through my reasoning about the following problem and questions will come up along the way.
- Relevant Equations
- Consider ##Al## and ##S## atoms and reason about the types of bonds formed between such atoms.
The first thing we notice is that we have a metal and a nonmetal, so we would think about an ionic model.
These elements form the ions ##Al^{3+}## and ##S^{2-}##.
These ions form a lattice structure and we get an ionic crystal.
But apparently no bond is perfectly ionic or covalent.
The electronegativities of aluminium and sulfur are 1.6 and 2.6, respectively. The difference is 1, which is a relatively low value, indicating a high covalent character to the bond formed. However, I am not sure if this difference in electronegativity is relevant when we are analyzing an ionic compound. I learned it in the context of ascertaining the ionic character of a covalent bond.
However, if we think in terms of polarization and polarizing power, then we have an ion with a relatively small radius and high charge (##Al^{3+}##) and an anion (##S^{2-}##). We should expect some distortion in the electron cloud of the anion and this occurrence means the bond has relatively high covalent character. This covalent character would be even larger if the anion were a larger, heavier atom. Such atoms have lower effective nuclear charge and more shells and their electron clouds are more easily distorted.
Question 1: Does any of this mean we can form a Lewis structure for a compound like ##Al_2S_3##?
After all, there is a Lewis structure for ##BF_3##, and ##B## forms ##B^{3+}## ions.
Instead of being an ionic compound it is covalent with a central boron that has an incomplete octet. It does, however, have high ionic character since the difference in electronegativity is ##\chi_{F}-\chi_{B}=2##.
Question 2: How do we know we can't have the same thing for ##Al_2S_3##?
Now, I'm asking this from the point of view of Lewis Structures and VSEPR.
It has been frustrating to study these topics because many things seem ad-hoc.
Here is another example
##N_2O##
One rule of thumb is to assume the central atom is of the element with the lowest ionization energy. That would be oxygen.
Apparently (by way of googling this molecule), another rule of thumb is to choose the element with the lowest electronegativity. That would be nitrogen.
So, how in the heck do we ever know, given a formula, what Lewis structure to build?
My guess is that these are all experimental results, and actually there is nothing that tells you whether oxygen or nitrogen is the central atom other than listing out exceptions upon exceptions to basic rules of thumb.
EDIT: just after writing this I realized that ##O## can't be the central atom because of another rule of sorts. If ##O## were the central atom it would have expanded valence. But only p-block atoms of elements in period 3 or later can have expanded valence because these elements have empty d-orbitals.
I just want to make sure that this is really the way to study this stuff. I'm self-studying Chemistry. It seems like a bunch of cases and some rules.
Question 3: Is there a light when one learns about quantum mechanics?
I do have one more question though. When we do write out the Lewis structure of ##N_2O##, we get
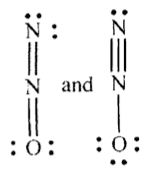
Question 4: Now, ##N## has five valence electrons. It appears only four are being shared in the structures above, and the fifth one went over to the oxygen. Either that or three electrons are being shared, and the fourth bond uses both electrons from ##N##.
These elements form the ions ##Al^{3+}## and ##S^{2-}##.
These ions form a lattice structure and we get an ionic crystal.
But apparently no bond is perfectly ionic or covalent.
The electronegativities of aluminium and sulfur are 1.6 and 2.6, respectively. The difference is 1, which is a relatively low value, indicating a high covalent character to the bond formed. However, I am not sure if this difference in electronegativity is relevant when we are analyzing an ionic compound. I learned it in the context of ascertaining the ionic character of a covalent bond.
However, if we think in terms of polarization and polarizing power, then we have an ion with a relatively small radius and high charge (##Al^{3+}##) and an anion (##S^{2-}##). We should expect some distortion in the electron cloud of the anion and this occurrence means the bond has relatively high covalent character. This covalent character would be even larger if the anion were a larger, heavier atom. Such atoms have lower effective nuclear charge and more shells and their electron clouds are more easily distorted.
Question 1: Does any of this mean we can form a Lewis structure for a compound like ##Al_2S_3##?
After all, there is a Lewis structure for ##BF_3##, and ##B## forms ##B^{3+}## ions.
Instead of being an ionic compound it is covalent with a central boron that has an incomplete octet. It does, however, have high ionic character since the difference in electronegativity is ##\chi_{F}-\chi_{B}=2##.
Question 2: How do we know we can't have the same thing for ##Al_2S_3##?
Now, I'm asking this from the point of view of Lewis Structures and VSEPR.
It has been frustrating to study these topics because many things seem ad-hoc.
Here is another example
##N_2O##
One rule of thumb is to assume the central atom is of the element with the lowest ionization energy. That would be oxygen.
Apparently (by way of googling this molecule), another rule of thumb is to choose the element with the lowest electronegativity. That would be nitrogen.
So, how in the heck do we ever know, given a formula, what Lewis structure to build?
My guess is that these are all experimental results, and actually there is nothing that tells you whether oxygen or nitrogen is the central atom other than listing out exceptions upon exceptions to basic rules of thumb.
EDIT: just after writing this I realized that ##O## can't be the central atom because of another rule of sorts. If ##O## were the central atom it would have expanded valence. But only p-block atoms of elements in period 3 or later can have expanded valence because these elements have empty d-orbitals.
I just want to make sure that this is really the way to study this stuff. I'm self-studying Chemistry. It seems like a bunch of cases and some rules.
Question 3: Is there a light when one learns about quantum mechanics?
I do have one more question though. When we do write out the Lewis structure of ##N_2O##, we get
Question 4: Now, ##N## has five valence electrons. It appears only four are being shared in the structures above, and the fifth one went over to the oxygen. Either that or three electrons are being shared, and the fourth bond uses both electrons from ##N##.
Last edited: