- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Who needs qubits? Factoring algorithm run on a probabilistic computer
In summary, the article discusses a new approach to factoring numbers using a probabilistic computer instead of qubits. This device uses discrete electronics and deep learning techniques to simulate a quantum computer, although it may not be scalable at quantum speeds. The discussion also references a previous question on Physics Forums about using a quantum computer for Shor's algorithm.
Computer science news on Phys.org
- #2
- 14,785
- 9,123
We have a similar kind of device at work that allows one to pretend they have a quantum computer but everything is done with discrete electronics and some magic or is that MAGIC and some discrete electronics.
- #3
anorlunda
Staff Emeritus
- 11,308
- 8,732
Thanks for sharing. It gets to a question I asked long ago on PF,
https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/making-a-quantum-computer-do-shors-algorithm.873585/
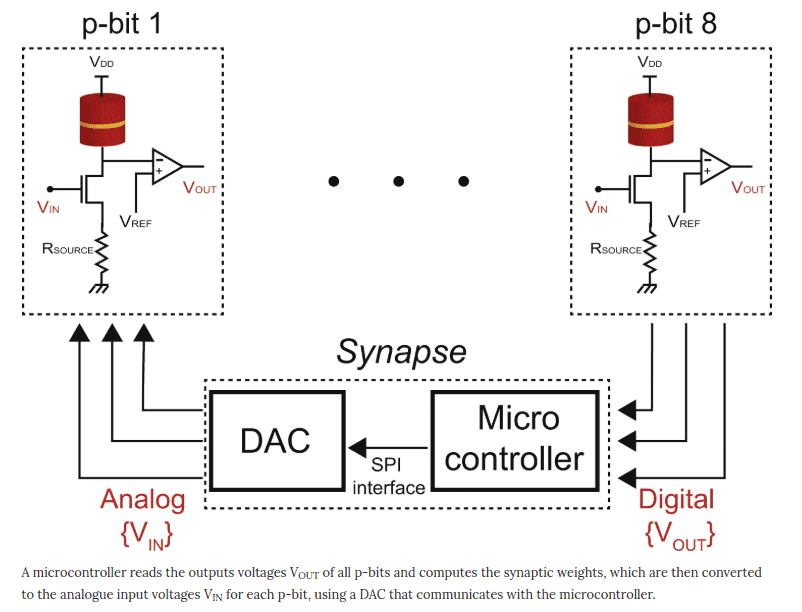
I never got an answer to that but this article does show how they did it. It appears that they made a neural net using conventional computers for the deep learning feedback and synapse adjustment. That's cheating because the conventional part won't scale with quantum speed.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1557-9/figures/5
https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/making-a-quantum-computer-do-shors-algorithm.873585/
I never got an answer to that but this article does show how they did it. It appears that they made a neural net using conventional computers for the deep learning feedback and synapse adjustment. That's cheating because the conventional part won't scale with quantum speed.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1557-9/figures/5
1. What is a qubit?
A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, similar to a classical bit in a traditional computer. However, while a classical bit can only store information as either a 0 or 1, a qubit can exist in a superposition of both states at the same time, allowing for the potential for faster and more efficient computing.
2. How does a factoring algorithm work on a probabilistic computer?
A factoring algorithm on a probabilistic computer utilizes the ability of qubits to exist in multiple states simultaneously to quickly calculate the prime factors of a large number. This is a task that would take a traditional computer a very long time to complete, but can be done much more efficiently using qubits.
3. What are some potential uses for qubits and factoring algorithms?
Qubits and factoring algorithms have the potential to revolutionize many industries, including cryptography, drug discovery, and financial modeling. They could also greatly improve the speed and efficiency of data processing and machine learning.
4. How does a probabilistic computer differ from a traditional computer?
A probabilistic computer, also known as a quantum computer, utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations. This allows for the potential for much faster and more efficient computing compared to traditional computers, which use classical bits to store and process information.
5. Who would benefit from the use of qubits and factoring algorithms?
The potential benefits of qubits and factoring algorithms extend to many industries and fields, including governments, businesses, and scientific research. Anyone who needs to process large amounts of data or solve complex problems could benefit from the use of these technologies.
Similar threads
-
Computing and Technology
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 2K
-
Quantum Physics
- Replies
- 22
- Views
- 604
Calculators
Repositories of Quantum Computing projects?
-
Computing and Technology
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 939
Insights
Quantum Computing for Beginners
-
Quantum Physics
- Replies
- 18
- Views
- 3K
-
Quantum Physics
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 774
-
Quantum Physics
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 1K
-
Computing and Technology
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 752
-
Quantum Physics
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 2K
-
Quantum Physics
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 704
-
Programming and Computer Science
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 1K
Share: