Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the necessity of defining a bound vector for position and velocity in vector equations, particularly in the context of a line in 3D space. Participants explore the roles of direction vectors and their significance in visualizing motion and changes in position.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
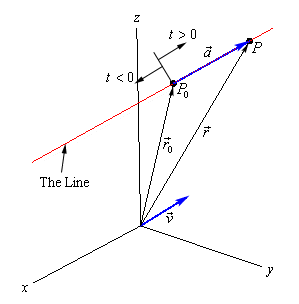
- Jon questions the need for a direction vector, v, in the vector equation for position, suggesting that vector a might suffice.
- Some participants seek clarification on the purpose of defining the position vector r and its relationship with vectors v and a.
- mathman points out a potential misunderstanding regarding the magnitudes and directions of vectors v and a, asking for their significance.
- Another participant explains that parallel vectors can be expressed as multiples of each other and introduces a parameter t that allows the position vector r to move along the line.
- A participant elaborates on the concept of free vectors and bound vectors, stating that bound vectors provide a clearer geometric representation of vector components and facilitate visualization of motion and velocity.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying levels of understanding regarding the necessity and purpose of bound vectors, with some seeking clarification and others providing explanations. The discussion remains unresolved, with no consensus on the fundamental question posed by Jon.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations in the clarity of definitions and assumptions regarding the vectors involved, as well as the specific context of the line being discussed. The significance of the parameter t and its implications for the position vector are also not fully resolved.