SUMMARY
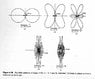
The discussion centers on the differences in radiation patterns of antennas, particularly small-loop antennas, as explained in the third edition of Kraus's book on antennas. The primary factor influencing these differences is the wavelength, which affects the phase relationship between closely spaced rod antennas that comprise the loop. As the wavelength changes, the radiation pattern shifts due to variations in the array factor and the phase of the antennas. The conversation also highlights the importance of loop circumference and its relationship to frequency in determining radiation characteristics.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of antenna theory and radiation patterns
- Familiarity with small-loop antennas and their configurations
- Knowledge of phase relationships in antenna arrays
- Basic principles of electromagnetic radiation
NEXT STEPS
- Study the chapter on small-loop antennas in the second edition of Kraus's book
- Explore the use of Eznec antenna simulation software for practical applications
- Research the effects of loop circumference on radiation patterns
- Learn about the impact of polarization on antenna radiation characteristics
USEFUL FOR
Electronics engineers, antenna designers, and students of telecommunications seeking to deepen their understanding of antenna radiation patterns and their dependencies on wavelength and configuration.