SUMMARY
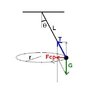
The discussion centers on the physics of a ball tethered to a post by a string, illustrating how centrifugal force and gravity interact as the ball spins. As the ball's angular speed (ω) increases, the tension in the string rises, creating both horizontal and vertical components. The vertical component counteracts gravity, allowing the ball to ascend if it exceeds gravitational force. The relationship between the angle of the string (θ), the radius of the circular path (r), and the forces acting on the ball is crucial in understanding this phenomenon.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of centripetal force and its components
- Familiarity with angular velocity (ω) and its implications
- Basic knowledge of vector components in physics
- Concept of tension in strings and its role in circular motion
NEXT STEPS
- Study the relationship between tension and angular velocity in circular motion
- Explore the concept of centripetal force in depth
- Learn about the effects of varying angles on circular motion dynamics
- Investigate real-world applications of centrifugal force in engineering
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the mechanics of circular motion and the forces involved in spinning objects.