- #1
bcarlson
- 6
- 0
EOMs for "T" Shaped Pendulum with Non-Conservative Force
I have a set of equations of motion I'm trying to derive. This problem represents a 2-d approximation of the real system that I'm trying to derive equations of motion for modeling purposes.
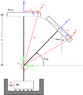
There is a base mass and a top mass.
The base mass is constrained to move only in the x direction and is connected by a linear spring to ground which is meant to produce forces that restore the mass to the x = 0 position. Friction is ignored.
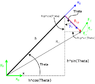
The top mass designated (the "T" shaped pendulum) can rotate about the point at the center of the base coordinate system. A torsional spring is operating on the pendulum to produce forces that restore it to the vertical position.
I've chosen my generalized coordinates to be x (corresponding to x-base) and theta (rotation of pendulum from horizontal).
I will include my derivations in reply to this post but my main question is whether I did the virtual work properly? Do I need to for any sort of moment-work?
I have a set of equations of motion I'm trying to derive. This problem represents a 2-d approximation of the real system that I'm trying to derive equations of motion for modeling purposes.
There is a base mass and a top mass.
The base mass is constrained to move only in the x direction and is connected by a linear spring to ground which is meant to produce forces that restore the mass to the x = 0 position. Friction is ignored.
The top mass designated (the "T" shaped pendulum) can rotate about the point at the center of the base coordinate system. A torsional spring is operating on the pendulum to produce forces that restore it to the vertical position.
I've chosen my generalized coordinates to be x (corresponding to x-base) and theta (rotation of pendulum from horizontal).
I will include my derivations in reply to this post but my main question is whether I did the virtual work properly? Do I need to for any sort of moment-work?