- #1
Mr.Bomzh
- 90
- 0
Hi , I am interested to know how would the magnetic field lines be formed and what effect each one of them would have to the one next to the other in such a configuration. I have two pairs of magnets.
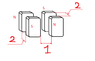
Distance between each magnet in a pair , numbered 2, is 2 mm. the distance between the two pairs of magnets , numbered 1 is 1cm.
In one pair the magnets stand NS in the other they are opposite SN, this is not a homework I was just interested what happens in such a configuration , if the distance between opposite magnets in a pair is smaller than that of the same opposite magnets between the pairs do most strength of field goes between the pair or is it shared also with the side pair even though it is further? I hope you understand my question , thank you :)
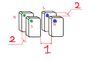
Distance between each magnet in a pair , numbered 2, is 2 mm. the distance between the two pairs of magnets , numbered 1 is 1cm.
In one pair the magnets stand NS in the other they are opposite SN, this is not a homework I was just interested what happens in such a configuration , if the distance between opposite magnets in a pair is smaller than that of the same opposite magnets between the pairs do most strength of field goes between the pair or is it shared also with the side pair even though it is further? I hope you understand my question , thank you :)