- #1
Lo.Lee.Ta.
- 217
- 0
1. "Students were instructed to mix the benzaldehyde and acetone starting materials in their conical vials before adding the ethanolic sodium hydroxide solution.
Why was this essential to the success of the reaction?
What would have been the most likely product formed if the sodium hydroxide solution were added to the vial first, followed by acetone and then waiting a few minutes to add the benzaldehyde?
Provide a balanced equation showing this reaction:"
2. From the reaction of NaOH with acetone, I thought the product would be
4-methyl-3-penten-3-one + 2H2O + NaOH.
Then I'm confused about what happens once benzaldehyde is added...
I'm wondering if the NaOH deprotonates the alpha carbons of 4-methyl-3-penten-3-one again, which would cause the benzaldehydes to add...
If another deprotonation occurs, I get this as the final product:
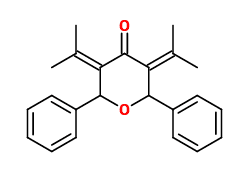
I thought the steric strain from the 2 hydroxyls might cause a dehydration reaction, which results in the ether bond...?
Not sure... This seems like too weird of a product to be right... Please help?!
Thanks! :)
Why was this essential to the success of the reaction?
What would have been the most likely product formed if the sodium hydroxide solution were added to the vial first, followed by acetone and then waiting a few minutes to add the benzaldehyde?
Provide a balanced equation showing this reaction:"
2. From the reaction of NaOH with acetone, I thought the product would be
4-methyl-3-penten-3-one + 2H2O + NaOH.
Then I'm confused about what happens once benzaldehyde is added...
I'm wondering if the NaOH deprotonates the alpha carbons of 4-methyl-3-penten-3-one again, which would cause the benzaldehydes to add...
If another deprotonation occurs, I get this as the final product:
I thought the steric strain from the 2 hydroxyls might cause a dehydration reaction, which results in the ether bond...?
Not sure... This seems like too weird of a product to be right... Please help?!
Thanks! :)