- #1
Blackhawk4560
- 19
- 0
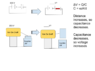
Question: If you charge a capacitor circuit and then separate the capacitor, does voltage increase beyond the initial source?
It seams counter intuitive that if you plug a 9 Volt battery into two metal plates and pull the plates apart that you'll get massive voltage spikes, but that's what the equations seem to point to...
You'll see a diagram of this attached,
Thanks for your time!
It seams counter intuitive that if you plug a 9 Volt battery into two metal plates and pull the plates apart that you'll get massive voltage spikes, but that's what the equations seem to point to...
You'll see a diagram of this attached,
Thanks for your time!