- #1
Moniz_not_Ernie
- 21
- 0
I couldn’t find a table of cumulative fission yields on the web, so I made one in a database simulation. Who might be interested?
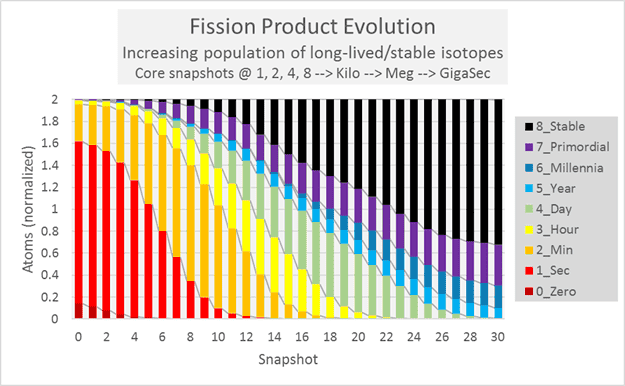
The full table covers the evolution of 1322 isotopes over 34 years. The results are in the form of 31 “snapshots” of the isotopic composition as the reactor ages from one second (20) to a GigaSec (230 seconds).
Here is a chart from the output table, highlighting a new field that groups the isotopes by half-life. It shows how the very hottest isotopes get swamped by their daughters as they cool. On the left, the fission of a 238-U atom produces two total fission fragments, 80% of which have half-lives of less than a minute. The remaining columns have populations normalized to that. On the right, the population of fission fragments is actually 2 billion+, over half of which are stable.
Data are available for 21 combinations of fuels and neutron speeds. (In fact, there were only 21 fission events in the whole simulation. I cloned each one 30 times.) The source data is also available. Coordinating the isotope, initial yield, and branching data from three separate sources was not trivial! The database is called the Integrated Fission Fragment Yield database. It will remain IFFY until some reputable source verifies and validates my work. Any takers?
The full table covers the evolution of 1322 isotopes over 34 years. The results are in the form of 31 “snapshots” of the isotopic composition as the reactor ages from one second (20) to a GigaSec (230 seconds).
Here is a chart from the output table, highlighting a new field that groups the isotopes by half-life. It shows how the very hottest isotopes get swamped by their daughters as they cool. On the left, the fission of a 238-U atom produces two total fission fragments, 80% of which have half-lives of less than a minute. The remaining columns have populations normalized to that. On the right, the population of fission fragments is actually 2 billion+, over half of which are stable.
Data are available for 21 combinations of fuels and neutron speeds. (In fact, there were only 21 fission events in the whole simulation. I cloned each one 30 times.) The source data is also available. Coordinating the isotope, initial yield, and branching data from three separate sources was not trivial! The database is called the Integrated Fission Fragment Yield database. It will remain IFFY until some reputable source verifies and validates my work. Any takers?