- #1
ulver48
Hello,
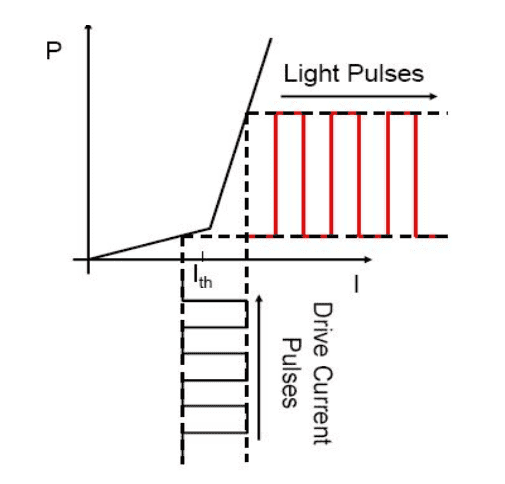
There is a thing I struggle to understand on laser physics. There is a modulation method called direct modulation for semiconductor lasers where by changing the current we modulate the light which is emitted form the laser cavity. There is a picture below
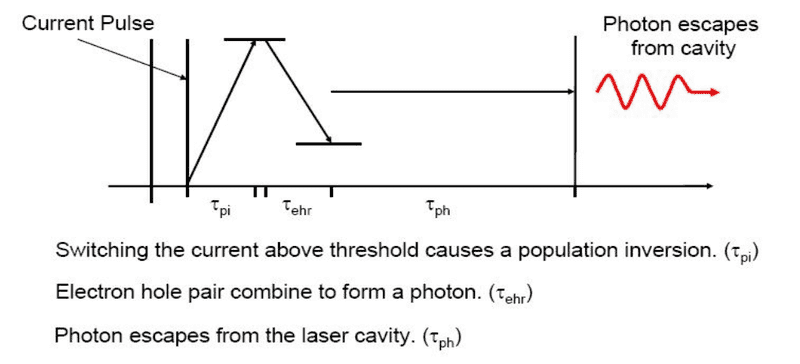
It is stated in bibliography that the fundamental limit as far as the modulation frequency is concerned is the inverse of the photon lifetime. This is shown in the following picture. Can someone explain to me why tph is the fundamental limit? Thank you for your time.
There is a thing I struggle to understand on laser physics. There is a modulation method called direct modulation for semiconductor lasers where by changing the current we modulate the light which is emitted form the laser cavity. There is a picture below
It is stated in bibliography that the fundamental limit as far as the modulation frequency is concerned is the inverse of the photon lifetime. This is shown in the following picture. Can someone explain to me why tph is the fundamental limit? Thank you for your time.