- #1
TomVu
- 1
- 0
Hello everyone, I have a problem while calculate dynamic for gyroscope system on bicycle. I use Lagrange's equation for modelling precession effect, with generalized coordinate is a angular, the applied generalized force will be a torque. The model of gyroscope system like picture below:
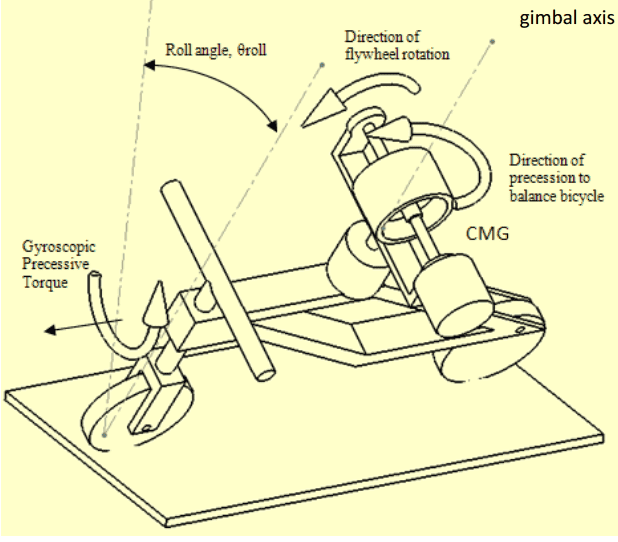 I've found it in many papers but just got only one equation like this one and I still not understood it:
I've found it in many papers but just got only one equation like this one and I still not understood it:
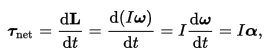
That equation above seem not related with the equation I have found (1). If you have any idea for solve this problem, please tell me. I would be very appreciated for your help.
- torque of gyro = angular momentum of gyro * angular velocity of gimbal axis (1)
That equation above seem not related with the equation I have found (1). If you have any idea for solve this problem, please tell me. I would be very appreciated for your help.