- #1
amama
- 7
- 1
Let's say you are riding a bike very fast, and then you sharply turn into a slide (where the bike is sliding perfectly sideways).
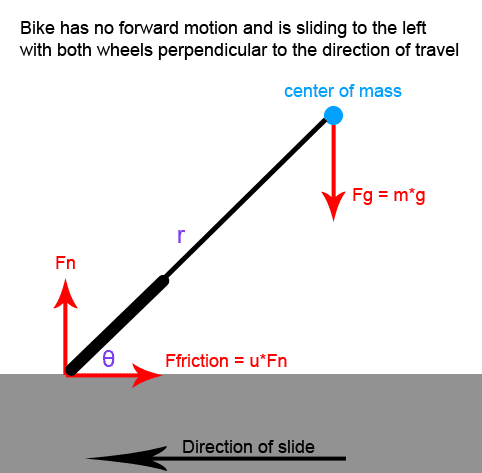
I'm trying to calculate the angle that the bike would be leaning at, but I'm having trouble creating the free body diagram.
Right now I have the normal force and friction force drawn where the wheels touch the ground. I also have the force from the weight drawn at the center of mass.
The approach I took is to calculate the torque around the wheel-contact point (pivot point) and set it equal to zero. However, right now, the only torque around the contact point is from the force of the weight, and there is nothing counteracting it, so the bike would fall. I would have guessed that the force of the friction would provide the force holding the bike up, but it doesn't provide any torque around the pivot point.
I'm guessing that I'm either missing a force or incorrectly locating the pivot point. Does anyone know where my error is?
I'm trying to calculate the angle that the bike would be leaning at, but I'm having trouble creating the free body diagram.
Right now I have the normal force and friction force drawn where the wheels touch the ground. I also have the force from the weight drawn at the center of mass.
The approach I took is to calculate the torque around the wheel-contact point (pivot point) and set it equal to zero. However, right now, the only torque around the contact point is from the force of the weight, and there is nothing counteracting it, so the bike would fall. I would have guessed that the force of the friction would provide the force holding the bike up, but it doesn't provide any torque around the pivot point.
I'm guessing that I'm either missing a force or incorrectly locating the pivot point. Does anyone know where my error is?
Last edited:

