- #1
Pushoam
- 962
- 51
- TL;DR Summary
- How does putting a cover affect the pressure inside a glass filled with air?
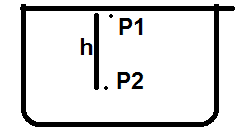
Let's consider an uncovered glass. Air particles are present in the glass.

$$ P_1 = P_a$$ $$P_2 =P_1 +\rho gh = P_a +\rho g h$$where ##P_A## is atmospheric pressuere and ##\rho ## is air density.
Now, if I cover the glass with a plastic card, then what is ## P_1##?
$$P_2 =P_1 +\rho gh $$
1) ## P_1 ## is pressure due to motion of air particles and the air particles near the cover interact with the cover and its speed may change and hence ##P_1## may be less or more than ##P_a##.
2) Following three forces are acting on the cover:
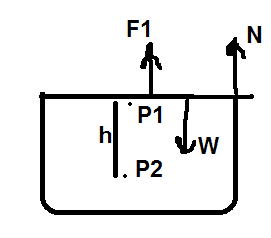
a) force due to pressure ##P_1## of air particles
b) normal force N due to glass walls
c) cover's weight W
Applying Newton's first law gives,
$$ P_1 A+ N = W$$ $$P_1 A = W - N$$
Now, since normal force is self-adjustable, let's take a light plastic card such that N = 0. Hence, in this case ##P_1 A = W ##.
For a plastic card with mass 20g and area 20cm2, ## P_1 = 10 Pa## which is lower than the atmospheric pressure.
So, the conclusion is: putting a cover reduces the pressure of air inside the glass. Is this correct?
$$ P_1 = P_a$$ $$P_2 =P_1 +\rho gh = P_a +\rho g h$$where ##P_A## is atmospheric pressuere and ##\rho ## is air density.
Now, if I cover the glass with a plastic card, then what is ## P_1##?
$$P_2 =P_1 +\rho gh $$
1) ## P_1 ## is pressure due to motion of air particles and the air particles near the cover interact with the cover and its speed may change and hence ##P_1## may be less or more than ##P_a##.
2) Following three forces are acting on the cover:
a) force due to pressure ##P_1## of air particles
b) normal force N due to glass walls
c) cover's weight W
Applying Newton's first law gives,
$$ P_1 A+ N = W$$ $$P_1 A = W - N$$
Now, since normal force is self-adjustable, let's take a light plastic card such that N = 0. Hence, in this case ##P_1 A = W ##.
For a plastic card with mass 20g and area 20cm2, ## P_1 = 10 Pa## which is lower than the atmospheric pressure.
So, the conclusion is: putting a cover reduces the pressure of air inside the glass. Is this correct?