- #1
ftft
- 21
- 0
My experience with data fitting is poor so I am in real need for help.
The potential in the following is periodic over [0,Pi]
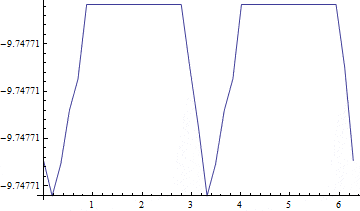
I need to find a fitting function that I can use to perform further mathematics. Fourier series does not work, but a 40-degree polynomial give the following fit
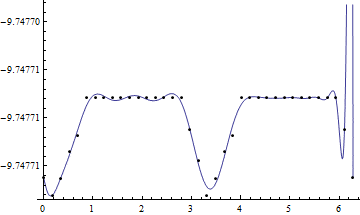
However, the polynomial does not preserve its periodicity over the cycle. Could someone please advice what I should do to get a good fitting function for my data?
The potential in the following is periodic over [0,Pi]
I need to find a fitting function that I can use to perform further mathematics. Fourier series does not work, but a 40-degree polynomial give the following fit
However, the polynomial does not preserve its periodicity over the cycle. Could someone please advice what I should do to get a good fitting function for my data?