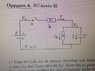
Voltage over a capacitor in a RC-circuit.
- Thread starter Nikitin
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Capacitor Rc-circuit Voltage
Click For Summary
The voltage across a capacitor in an RC circuit is expressed as Vc = Q/C, where Q is the charge and C is the capacitance. This relationship holds because both the capacitor and resistor are connected between the same two nodes, ensuring they share the same voltage. The electric field created by the charges on the capacitor plates is conservative, meaning the work done to move a charge between two points is independent of the path taken. Therefore, the potential difference remains consistent whether the charge travels through the capacitor or the resistor. Understanding these principles clarifies why the voltage across both components is identical.
Similar threads
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 5 ·