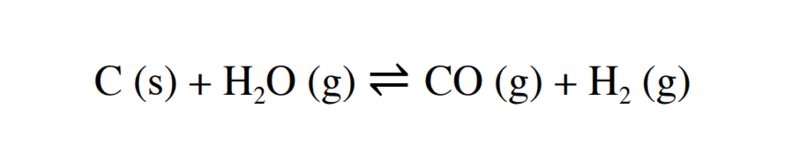SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the principles of chemical equilibrium, specifically addressing reactions involving multiple phases, such as solids, liquids, and gases. Participants confirm that the activity of solids is considered to be equal to 1 when writing equilibrium expressions. The formula for chemical equilibrium must account for the phases present, and the concentration of solids is not included in the equilibrium constant expression. Key rules for writing these formulas were reiterated, emphasizing the importance of phase consideration.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of chemical equilibrium concepts
- Familiarity with phase states: solid, liquid, gas
- Knowledge of equilibrium constant expressions
- Basic chemistry principles regarding reaction dynamics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of equilibrium constant expressions for heterogeneous reactions
- Learn about the role of activity in chemical equilibria
- Explore examples of chemical reactions involving multiple phases
- Investigate the impact of temperature and pressure on equilibrium positions
USEFUL FOR
Chemistry students, educators, and professionals involved in chemical research or industrial applications who seek to deepen their understanding of chemical equilibrium in multi-phase reactions.