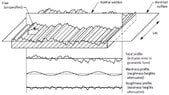
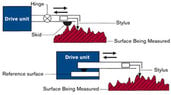
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around alternative methods for measuring surface roughness of 3D printed specimens, particularly in the context of a school project. Participants explore various techniques that could be employed using equipment commonly available in a high school setting, rather than relying on standard measurement tools.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- Some participants suggest comparing the surface roughness of items to each other rather than to an absolute standard, indicating that this may simplify the measurement process.
- One participant proposes using flow resistance in a tube as a comparative method for measuring roughness, noting that friction or stiction comparisons could also be explored, although these methods may be variable.
- Another idea involves using a pencil to stroke the surfaces of two samples and comparing the sound produced, with louder sounds indicating greater roughness.
- A participant mentions the possibility of fabricating a device using compressed air to measure surface texture based on airflow differences due to surface irregularities.
- Some participants discuss the potential use of optical microscopes for image analysis, raising questions about how to measure the depth of surface irregularities with such tools.
- There is mention of using laser scattering techniques to differentiate roughness ranges, with a focus on whether the interest lies in the scale or depth of roughness.
- Concerns are raised about the complexity of defining and measuring surface texture, including the need for a repeatable and accurate process.
- One participant suggests that using a standard for comparison could help in achieving replicable results.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express a variety of methods and approaches, with no consensus on a single best method for measuring surface roughness. Multiple competing views and techniques remain under discussion.
Contextual Notes
Participants acknowledge limitations in their proposed methods, including the variability of results and the need for calibration standards. There is also recognition of the complexity involved in accurately measuring surface texture.
Who May Find This Useful
This discussion may be useful for students and educators interested in practical approaches to measuring surface roughness, as well as those exploring alternative methods in experimental settings.