songoku
- 2,512
- 394
- Homework Statement
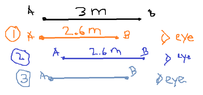
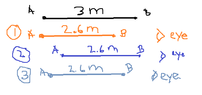
- The front of a spacecraft forms a point at an angle of 60 degrees. As the spacecraft increases speed, what happens to this angle as observed in the rest frame?
A. It stays the same.
B. It decreases.
C. It increases.
D. It decreases only if the spacecraft is going to the left.
E. It decreases only if the spacecraft is going to the right
- Relevant Equations
- Time dilation
Length contraction
My answer is (A) since I think the motion of the spacecraft will alter the length of the spacecraft (length contraction) but not changing the orientation so the angle will stay the same
But my teacher said my answer is wrong. What is my mistake?
Thanks
But my teacher said my answer is wrong. What is my mistake?
Thanks