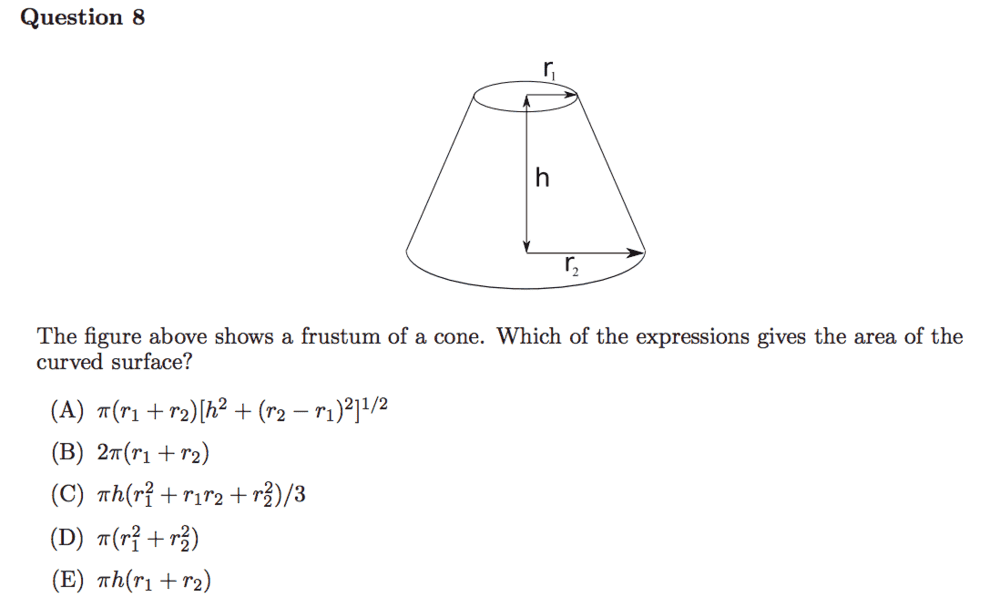SUMMARY
The discussion centers on calculating the surface area of a frustrum using the Pappus-Guldinus theorem. The surface area A of a surface of revolution is defined as A = sd, where s is the arc length and d is the distance traveled by the centroid. Participants explore various options for the surface area formula, ultimately concluding that option A is correct, while option E, despite appearing plausible, does not account for the necessary dependencies on height (h). The conversation emphasizes the importance of integrals and the Pythagorean theorem in deriving the correct formula.
PREREQUISITES
- Pappus-Guldinus theorem
- Understanding of surface area calculations
- Basic knowledge of integrals
- Pythagorean theorem application
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Pappus-Guldinus theorem in detail
- Learn how to compute surface areas using integrals
- Explore examples of calculating the surface area of various solids of revolution
- Investigate the implications of dimensional analysis in geometry problems
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in mathematics and physics, particularly those focusing on geometry, calculus, and surface area calculations.