SUMMARY
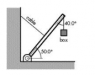
The discussion focuses on calculating the tension in a cable supporting a 20 kg uniform beam and the force on a hinge when a 50 kg box is suspended from it. The correct approach involves drawing a free body diagram and applying static equilibrium equations: ΣFx = 0, ΣFy = 0, and ΣMp = 0. An initial attempt at calculation yielded a tension of 656N, but the solution emphasizes the importance of methodical problem-solving rather than guesswork.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of static equilibrium principles
- Knowledge of free body diagrams
- Familiarity with forces and moments in physics
- Basic algebra for solving equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study how to construct free body diagrams for complex systems
- Learn about static equilibrium equations in detail
- Explore tension calculations in various mechanical systems
- Investigate the effects of different angles on tension and force distribution
USEFUL FOR
Students in physics or engineering courses, particularly those studying mechanics, as well as educators looking for problem-solving strategies in static equilibrium scenarios.