SUMMARY
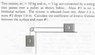
This discussion focuses on calculating the coefficient of kinetic friction in a system involving two masses connected by a string. The key takeaway is the importance of correctly defining the direction of acceleration in relation to the forces acting on each mass. The tension in the string remains constant, but the sign convention for acceleration must be consistent across both masses to avoid mathematical errors. The concept of "acceleration constraint" is crucial, as it dictates that the accelerations of the two masses are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
PREREQUISITES
- Newton's Second Law of Motion
- Understanding of tension in strings
- Concept of acceleration constraints in connected systems
- Free body diagram analysis
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Newton's Second Law in multi-mass systems
- Learn about free body diagrams and their role in solving physics problems
- Explore the concept of tension in pulleys and connected masses
- Investigate the implications of sign conventions in physics equations
USEFUL FOR
Students studying mechanics, physics educators, and anyone involved in solving problems related to forces and motion in connected systems.