- #1
Sophie87
- 3
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Calculate consumption, displacement and speed using given standard values in pneumatic cylinders and pipes (ISO 155552 Standard and ANSI B31.3 Standard).
I've been given three tables on different standards in pneumatics and the following values:
Force of advance= 50 kgf
Total Displacement: 3cm
Displacement: 45 seconds
Normal atmospheric conditions include Tn= 20 degrees Celsius and Pn= 1.03 kgf/cm2
The temperature of operation: 10 degrees above the environment temperature (dry-bulb)
From the table of unit consumption, calculate the total consumption and the discharge demanded by the cylinder. Speed of the air in the pipes: as per standards. Speed of the air in the hoses: as per standards. Calculate the diameters of the pipe and hoses. Select the most appropriate standardized piping based on the calculated diameter.
- Relevant Equations
- kgf/cm^2 = 50/(3^2) = 5.6 rounded up.
I calculated the value of kgf/cm^2 from given values. In the second table (Force exerted by the pneumatic cylinders) I see my value 5.6 exactly but how do I then read the table to get the diameter of the cylinder and then the rod?
I then am stuck on how to calculate the total consumption, displacement and speed of cylinders, pipes and hoses as I didn't learn this in class.
Can anyone help explain this for me?
Below are images of the table standards:
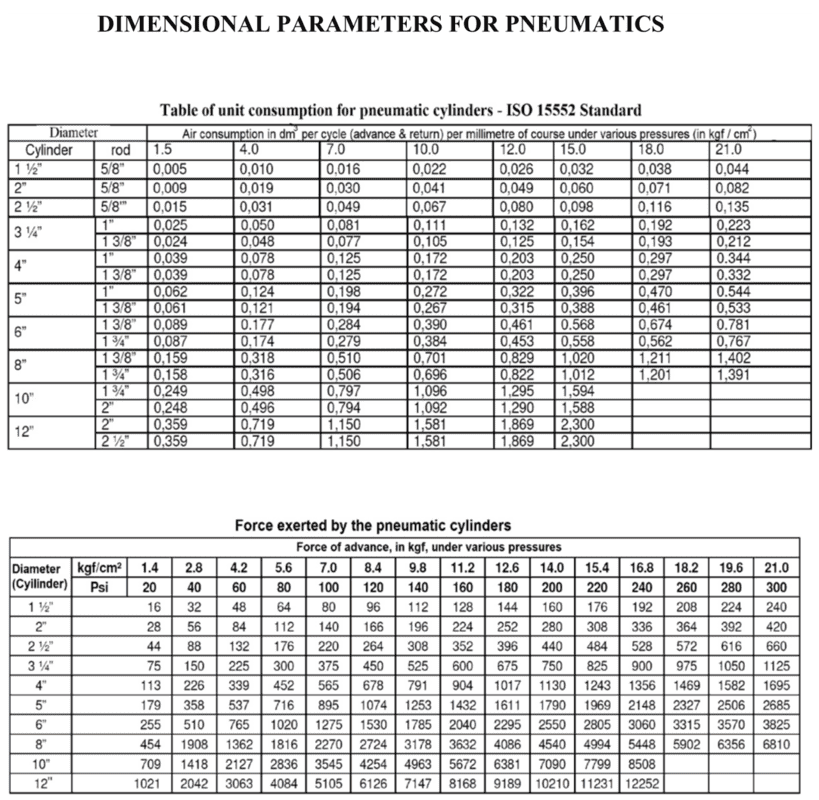
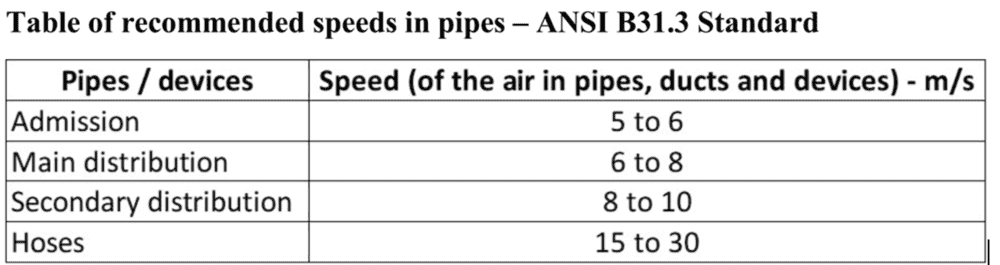
I then am stuck on how to calculate the total consumption, displacement and speed of cylinders, pipes and hoses as I didn't learn this in class.
Can anyone help explain this for me?
Below are images of the table standards: