Homework Help Overview
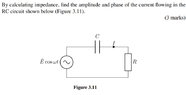
The discussion revolves around calculating the impedance in an RC circuit, focusing on the relationship between resistance, capacitance, and complex numbers in the context of alternating current analysis.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Mathematical reasoning, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- The original poster attempts to derive the amplitude and phase of the current using the impedance formula but seeks clarification on how to apply it. Participants inquire about the use of complex numbers in expressing impedance.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants exploring the representation of impedance as a complex number. Some guidance has been offered regarding the use of complex numbers, but no consensus or resolution has been reached yet.
Contextual Notes
There is a reference to external resources for further understanding of RC circuit analysis, indicating that participants may be considering additional information to aid their discussion.