SUMMARY
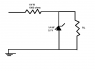
Modifying the load resistor in a Zener diode circuit significantly impacts circuit behavior. When the load resistor (RL) is short-circuited, the voltage across the Zener diode becomes zero, and the entire supply voltage is dropped across the series resistor (1000 Ω), potentially exceeding its power rating. If the load resistor is removed, the Zener diode conducts current, and the voltage drop across it equals its Zener voltage, allowing for current calculation through the series resistor. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for safe circuit design and component selection.
PREREQUISITES
- Zener diode operation and characteristics
- Basic circuit analysis techniques
- Power dissipation calculations (P=V^2/R, P=I^2R)
- Understanding of series and parallel resistor configurations
NEXT STEPS
- Study Zener diode reverse bias operation and breakdown voltage
- Learn about power ratings and thermal management in resistors
- Explore circuit simulation tools like LTspice for practical analysis
- Investigate the effects of varying load conditions on Zener circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electronics students, circuit designers, and engineers working with voltage regulation and power supply circuits will benefit from this discussion.