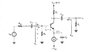
Why Are RL and RC Considered Parallel in Common Emitter Amplifier AC Analysis?
- Thread starter exis
- Start date
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
In AC analysis of common emitter amplifiers, the load resistor (RL) and collector resistor (RC) are treated as parallel components when calculating the output voltage (Vo) in response to changes in collector current (IC) due to input signal (isig). This approach is valid because, during AC analysis, the coupling capacitor (Cc2) is assumed to be a short circuit, creating a low impedance path between ground and Vcc. This assumption simplifies the analysis and accurately reflects the behavior of the circuit under AC conditions.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of common emitter amplifier configurations
- Familiarity with AC analysis techniques in electronics
- Knowledge of impedance concepts in circuit analysis
- Basic principles of coupling capacitors in amplifier circuits
- Study the impact of coupling capacitors on AC signal integrity
- Learn about the role of load and collector resistors in amplifier design
- Explore advanced AC analysis techniques for transistor circuits
- Investigate the effects of varying input signals on output voltage in amplifiers
Electronics students, circuit designers, and engineers involved in amplifier design and analysis, particularly those focusing on common emitter configurations.
Similar threads
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 17 ·
- · Replies 25 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 1 ·