Pouyan
- 103
- 8
- Homework Statement
- In the circuit shown below, I will determine the voltage between points P and Q. The answer is given but my problem is that I can not find the total resistance in the circuit.
- Relevant Equations
- V=R*I
The true answer is : The voltage between P and Q is 1.5 V.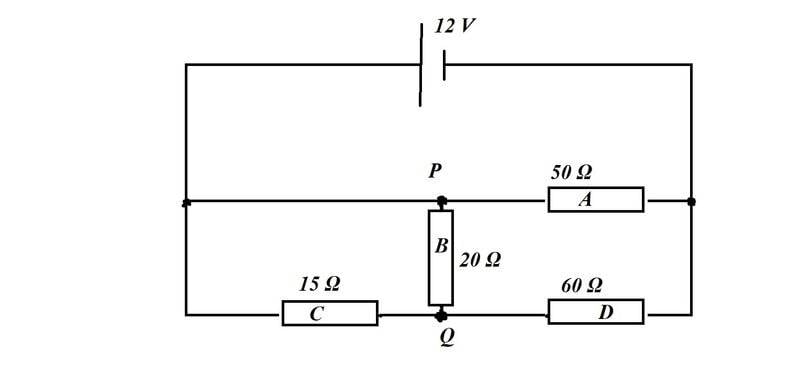
I got stuck finding the total resistance. My question is:
Is B parallel to both A and C?
Is C parallel to D ?
I tried many ways to find the total R but failed!
My first attempt:
I say the system ABD is in serie with C:
$$\frac{1}{R_{A}} +\frac{1}{R_{B}} + \frac{1}{R_{C}} $$
and $$R_{ABD}=11.54\Omega $$
together with Rc :
$$R_{C}+R_{ABD}=26.54\Omega $$
$$I_{total}=\frac{12}{26.54}\textit{A}=0.45A$$
In this case when Rc is in seire with RABD, then the current is the same in both systems and the voltage at Rc = 15*0.45V=6.75V!
The voltage in the ABC is (12-6.75)V = 5.25 V.
The current IA is then at RA = $$\frac{5.25}{50} A$$
But it's not correct! since I know that VPQ=1.5 V!
How can I get the total R ?