Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around understanding force body diagrams in the context of two-body collisions, specifically examining Newton's third law and the forces experienced by each body during the collision. Participants explore both elastic and inelastic collisions, the role of accelerations, initial velocities, and the duration of the collision.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
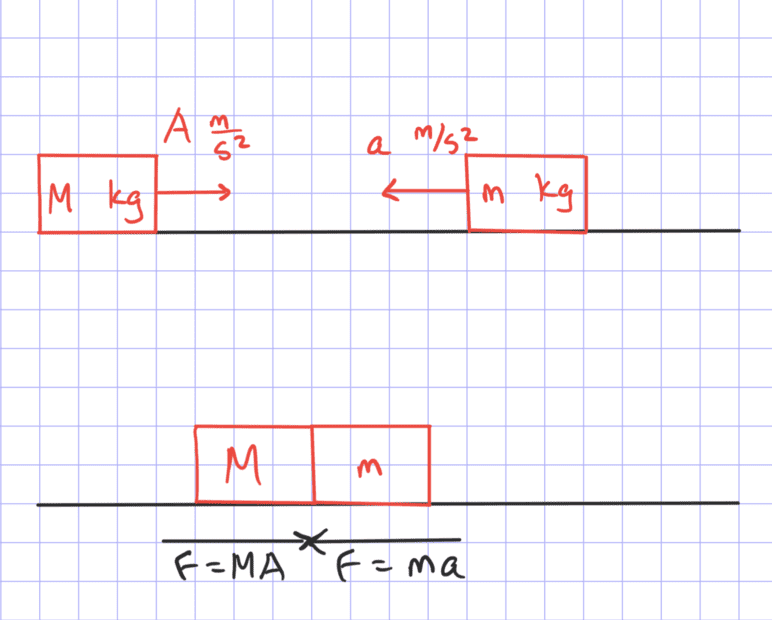
- One participant suggests that during a collision, both bodies will experience the same force, questioning whether this force can be expressed as F = MA + ma and how to represent it in a force body diagram.
- Another participant argues that the accelerations of the masses must be due to external forces and that the equal and opposite forces during a collision do not directly relate to these external forces.
- Several participants emphasize the need for additional information, such as initial velocities and the duration of the collision, to fully understand the forces involved.
- A participant provides a numerical example with specific masses, velocities, and accelerations, asking how to use this information to determine the forces during the collision.
- Another participant explains that the change in speed during the collision can be used to calculate average acceleration and subsequently the force acting on each object.
- One participant notes that if the forces are only due to mutual interaction, Newton's third law applies, and they present equations of motion for the bodies, emphasizing momentum conservation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the necessity of external forces and the information required to analyze the collision. There is no consensus on how to represent the forces in the body diagram or the specific calculations needed, indicating ongoing debate and exploration of the topic.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight limitations in the discussion, such as the need for initial velocities and collision duration, which are not fully addressed. The discussion remains open-ended regarding the exact calculations and representations of forces.