Discussion Overview
The discussion centers on the color of copper nitrate and its relationship to the compound's structural and electronic properties, particularly focusing on the octahedral geometry and the behavior of d orbitals. Participants explore concepts related to ligand field theory, crystal field splitting, and the effects of molarity on color intensity.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
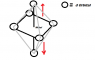
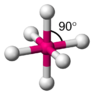
- Some participants suggest that the intensity of the blue color in copper nitrate is related to the distance between vertical d orbitals in an octahedral structure, with greater distances potentially leading to more intense colors.
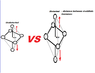
- Others propose that changes in Ligand Field Stabilization Energy (LFSE) from high spin to low spin configurations affect electron distribution in the d orbitals, influencing color intensity.
- There is a discussion about the role of ligands versus the central atom in absorbing and emitting energy, with some asserting that it is primarily the central atom that is responsible.
- One participant notes that the hydration of copper in solution and solid form may play a significant role in its color properties.
- Concerns are raised about how changing the molarity of copper nitrate affects color intensity, with observations that higher concentrations yield brighter colors.
- Some participants mention that the color of copper complexes results from both d-d transitions and charge transfer transitions from ligands to the copper atom, emphasizing the complexity of the interactions involved.
- There is a discussion about the nature of d-d transitions being weak due to being electric dipole forbidden, and how vibronic coupling may influence transition intensity.
- A later reply highlights that the specific d-d transition related to visible light absorption is affected by the energy difference between certain d orbitals, which can shift with changes in the octahedral geometry.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the mechanisms behind the color of copper nitrate, particularly regarding the roles of ligands and the central atom, as well as the implications of LFSE. There is no consensus on the exact relationship between structure, electron transitions, and color intensity.
Contextual Notes
Some participants note potential inaccuracies in the terminology used in external references, such as misclassifying cobalt as a ligand. Additionally, the discussion acknowledges that the understanding of color intensity may depend on various factors, including the specific electronic configurations and the nature of the ligands involved.