SweatingBear
- 119
- 0
We have the following trapezoid:
View attachment 1201
The question is to find the length of the fourth side when the area of trapezoid is maximized.
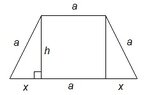
I realize we will not be able to find a numerical value for the fourth side due to the given information (rather, lack thereof). So we are essentially going have to find, through calculus, an algebraic relationship between the fourth side and the given side, $$a$$.
First and foremost, we need to write an equation for the area. The problem however is that we will not be able to express the function in simply one variable. This is where I am stuck: Since the function will depend on several variables, how can we tell which variable we ought to be taking the derivative with respect to? This is normally, from what I have experienced, the most difficult task i.e. to realize which variable one should take the derivative of.
Here's a spontaneous thought: Since we are looking for the relationship between the fourth side and the side $$a$$, it would be wise to express the function in terms of the mentioned sides. Thus, when we take the derivative and equate it to zero, we ought to be able to find some kind of relationship between the aforementioned sides.
What do you think forum? Share your insights!
View attachment 1201
The question is to find the length of the fourth side when the area of trapezoid is maximized.
I realize we will not be able to find a numerical value for the fourth side due to the given information (rather, lack thereof). So we are essentially going have to find, through calculus, an algebraic relationship between the fourth side and the given side, $$a$$.
First and foremost, we need to write an equation for the area. The problem however is that we will not be able to express the function in simply one variable. This is where I am stuck: Since the function will depend on several variables, how can we tell which variable we ought to be taking the derivative with respect to? This is normally, from what I have experienced, the most difficult task i.e. to realize which variable one should take the derivative of.
Here's a spontaneous thought: Since we are looking for the relationship between the fourth side and the side $$a$$, it would be wise to express the function in terms of the mentioned sides. Thus, when we take the derivative and equate it to zero, we ought to be able to find some kind of relationship between the aforementioned sides.
What do you think forum? Share your insights!