jjiimmyy101
- 74
- 0
I solved the first one...
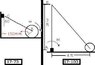
Problem 17-103 -- The two pin-connected bars each have a weight of 10 lb/ft. If a moment of M = 60 lb*ft is applied to bar AB, determine the initial vertical reaction at C and the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at B. Neglect the size of the roller at C. The bars are initially at rest. [By= 18.75 lb ; Cy = 31.25]
What I've done so far:
\sum Fx = max = 25(0.6) + Bx + 15(0.6) = 0
\sum Fy = may = -25(0.8) + Cy +By - 15(0.8) = 0
\sum MB = 0 = -60 -25(0.8)(2.5) + Cy(5) -15(0.6)(1.5)= 0
*I've taken my axis to be rotated (x-axis along BC, y-axis perpendicular to that)
* ax, ay, MB = 0 because it is initially at rest
*I've done something wrong (but I don't know what) because I keep getting the wrong answer. Any suggestions for this one?
Thanks for taking the time to read and answer this.
Problem 17-103 -- The two pin-connected bars each have a weight of 10 lb/ft. If a moment of M = 60 lb*ft is applied to bar AB, determine the initial vertical reaction at C and the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at B. Neglect the size of the roller at C. The bars are initially at rest. [By= 18.75 lb ; Cy = 31.25]
What I've done so far:
\sum Fx = max = 25(0.6) + Bx + 15(0.6) = 0
\sum Fy = may = -25(0.8) + Cy +By - 15(0.8) = 0
\sum MB = 0 = -60 -25(0.8)(2.5) + Cy(5) -15(0.6)(1.5)= 0
*I've taken my axis to be rotated (x-axis along BC, y-axis perpendicular to that)
* ax, ay, MB = 0 because it is initially at rest
*I've done something wrong (but I don't know what) because I keep getting the wrong answer. Any suggestions for this one?
Thanks for taking the time to read and answer this.
Attachments
Last edited: