SUMMARY
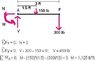
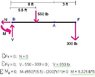
The discussion centers on calculating the resultant internal loadings in a jib crane, specifically at cross sections A, B, and C. The boom DF and column DE each have a uniform weight of 50 lb/ft, and the hoist and load together weigh 300 lb. The correct calculation for the force acting on beam DF was determined to be 650 lb, derived from multiplying the weight per foot by the length of the beam. Additionally, the downward force at point D was confirmed to be 250 lb, calculated from the 5 feet of column above cross-section C.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of static equilibrium in structures
- Familiarity with jib crane mechanics
- Knowledge of force distribution and load calculations
- Ability to interpret engineering diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study static equilibrium principles in structural engineering
- Learn about load calculations for cranes and hoisting systems
- Explore the effects of uniform loads on beams
- Investigate the use of free-body diagrams in structural analysis
USEFUL FOR
Structural engineers, crane operators, and students studying mechanical engineering principles will benefit from this discussion, particularly those focused on load analysis and crane operation safety.