Py3_3
- 1
- 0
Hello,
i'm doing a project where the goal is to get the relative position of a space object to the earth, roughly. Basically, i want to say that this object is currently e.g. above New York.
The data for any given space object that i have is
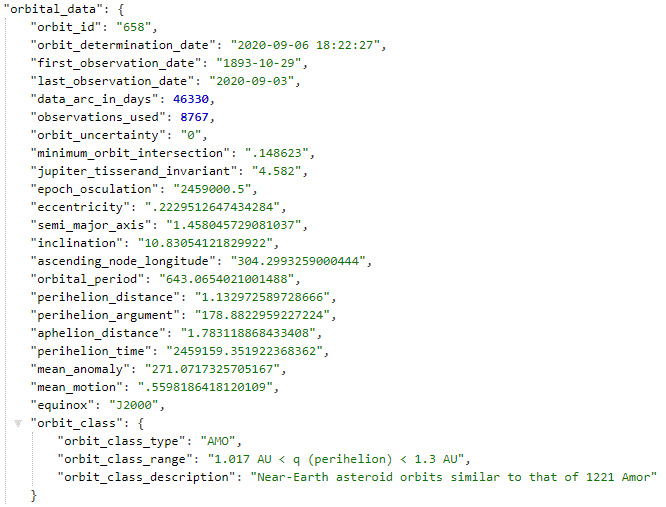
(It's sourced from an NASA API). The specific values are not important, just an example object.
I know nothing about how orbits are calculated and such, but I'm a pretty math-savvy guy and i'd be willing to research and learn it myself. But i don't want to spend 3 days digging into this stuff only to realize that what i want to do is not possible with the information i have.
So basically my question is the title. Also if you want to give me some pointers which of those values are important to me that would be amazing too.
Thanks in advance!
<Moderator's note: do not use external image servers. Upload your images to PhysicsForums.>
i'm doing a project where the goal is to get the relative position of a space object to the earth, roughly. Basically, i want to say that this object is currently e.g. above New York.
The data for any given space object that i have is
(It's sourced from an NASA API). The specific values are not important, just an example object.
I know nothing about how orbits are calculated and such, but I'm a pretty math-savvy guy and i'd be willing to research and learn it myself. But i don't want to spend 3 days digging into this stuff only to realize that what i want to do is not possible with the information i have.
So basically my question is the title. Also if you want to give me some pointers which of those values are important to me that would be amazing too.
Thanks in advance!
<Moderator's note: do not use external image servers. Upload your images to PhysicsForums.>
Last edited by a moderator: