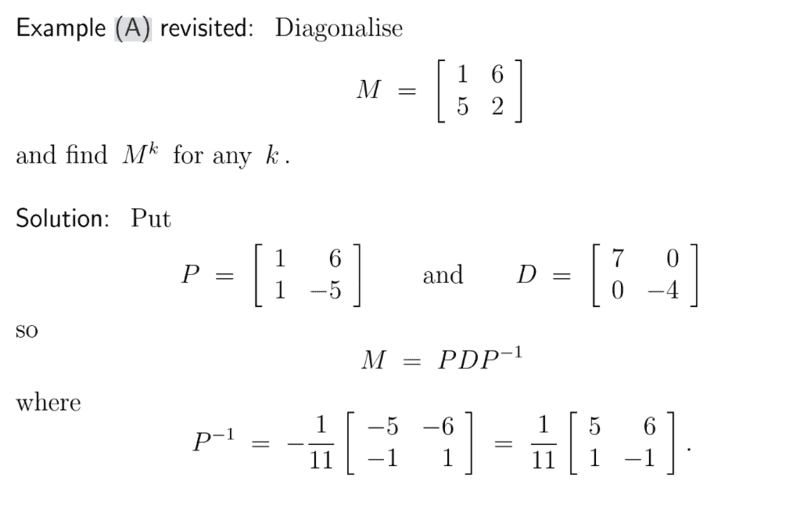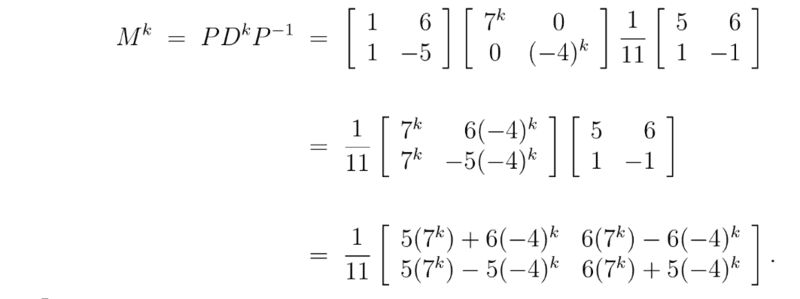Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around the process of diagonalizing a matrix, specifically focusing on the derivation of matrices P and D, as well as the implications of raising the matrix M to the power of k.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants inquire about the origins of matrices P and D in the diagonalization process and question why only the second matrix is raised to the power of k. There are mentions of calculating eigenvalues and using the Gauss-Jordan algorithm to solve related equations.
Discussion Status
Some participants have provided insights into the calculation of eigenvalues and the structure of the diagonalization process, while others continue to seek clarification on specific points, indicating an ongoing exploration of the topic.
Contextual Notes
There are indications of confusion regarding terminology and notation, as well as a playful exchange about language use, which may reflect the informal nature of the discussion.