- #1
Zach Hughes
- 2
- 0
I'm at wits end. I hate WileyPlus. Part A, B and C are correct. I cannot figure out what Part D is -- all of the answers I am getting are wrong.

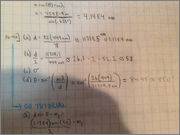
Zach Hughes said:I'm at wits end. I hate WileyPlus. Part A, B and C are correct. I cannot figure out what Part D is -- all of the answers I am getting are wrong.Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
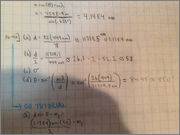
Double-slit diffraction is a phenomenon that occurs when a beam of light or particles passes through two parallel slits and produces an interference pattern on a screen. It is a demonstration of the wave-like nature of light and particles.
The greatest angle for minimum diffraction, also known as the angle of diffraction minimum, can be calculated using the equation sinθ = mλ/d, where θ is the angle of diffraction, m is the order of the diffraction pattern, λ is the wavelength of the light or particles, and d is the distance between the two slits. By finding the value of θ for m = 0, the greatest angle for minimum diffraction can be determined.
The angle of diffraction minimum is important because it determines the smallest angle at which the diffraction pattern can be observed. This angle can be used to calculate the wavelength of the light or particles passing through the slits, which is important for understanding the behavior of light and particles in various experiments and applications.
As the distance between the slits increases, the angle of diffraction minimum decreases. This is because the diffraction pattern becomes wider and the peaks become less pronounced, making it more difficult to determine the angle of minimum diffraction. Conversely, as the distance between the slits decreases, the angle of diffraction minimum increases.
Yes, the double-slit diffraction experiment can be performed with any type of coherent light or particles, such as lasers, electrons, or even atoms. The only requirement is that the light or particles must have a consistent wavelength and be able to pass through the slits without being significantly scattered or absorbed.