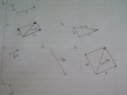
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the correctness of drawn geometric representations related to vector operations, specifically focusing on the application of the parallelogram law and vector addition/subtraction. Participants seek clarification on their drawings and the methodology for representing vectors accurately.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Technical explanation, Debate/contested, Homework-related, Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant asks for confirmation on the accuracy of their drawings and expresses difficulty with part (f).
- Another participant questions whether the direction of vector b should be reversed in their drawing.
- A participant explains two methods for understanding vector subtraction, emphasizing the tip-to-tail method and the tail-to-tail method.
- Some participants agree that vector b should be represented in the opposite direction as -b, confirming the correctness of the drawing.
- One participant suggests that part (f) can be approached by flipping vector a to -a and connecting it to the tail of 2b, which is drawn twice in length.
- A later reply emphasizes the need to specify which part of -a is connected to 2b, indicating a potential point of confusion.
- Another participant expresses satisfaction with the drawings, indicating they appear correct.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the methods for drawing the vectors and the correctness of certain representations, but there are points of clarification needed regarding the connections of vectors, particularly in part (f). Multiple views on the representation of vector directions remain present.
Contextual Notes
Some assumptions about vector directionality and connection points are not explicitly stated, which may lead to varying interpretations of the drawings.