SUMMARY
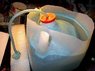
This discussion focuses on the efficient collection of hydrogen from water through electrolysis, utilizing a dome-shaped apparatus with alternating copper and zinc plates as electrodes. The participants emphasize the importance of separating hydrogen and oxygen gases during collection to prevent explosive mixtures. Key insights include the optimal voltage and current settings for electrolysis, with recommendations to use lower voltages (around 1.5V) to avoid damaging equipment. Additionally, the discussion highlights the necessity of using inert materials for the anode to prevent degradation during the process.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electrolysis principles and processes
- Familiarity with electrode materials and their properties
- Knowledge of voltage and current relationships in electrochemical cells
- Basic safety protocols for handling gases and electrical equipment
NEXT STEPS
- Research the effects of different electrode materials on electrolysis efficiency
- Learn about safe gas collection techniques for hydrogen and oxygen
- Investigate the use of pulse-width modulation for voltage regulation in electrolysis
- Explore the implications of using AC versus DC in electrolysis processes
USEFUL FOR
Individuals interested in electrochemistry, hobbyists experimenting with hydrogen production, and those seeking safe methods for gas collection and electrolysis optimization.