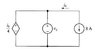
Electric Circuits: Find Vg & Why is it -2V?
- Thread starter sevag00
- Start date
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
The voltage Vg in the given electric circuit is determined to be -2V, indicating that the terminals are incorrectly oriented in the diagram. The negative voltage signifies that the positive terminal is actually at a lower potential than the negative terminal, which is a common occurrence in circuit analysis. The calculations performed, including the current ib of 8A and the derived voltage Vx of 2V, confirm the validity of the answer provided in the textbook.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of basic electric circuit theory
- Familiarity with voltage polarity and its implications
- Knowledge of current direction and its effect on circuit analysis
- Ability to interpret circuit diagrams accurately
- Study the principles of voltage sources and their configurations
- Learn about Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and its applications
- Explore the concept of controlled sources in electrical circuits
- Review examples of circuit analysis involving negative voltages
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in analyzing or troubleshooting electric circuits.