- #1
justin___
- 2
- 2
- Homework Statement
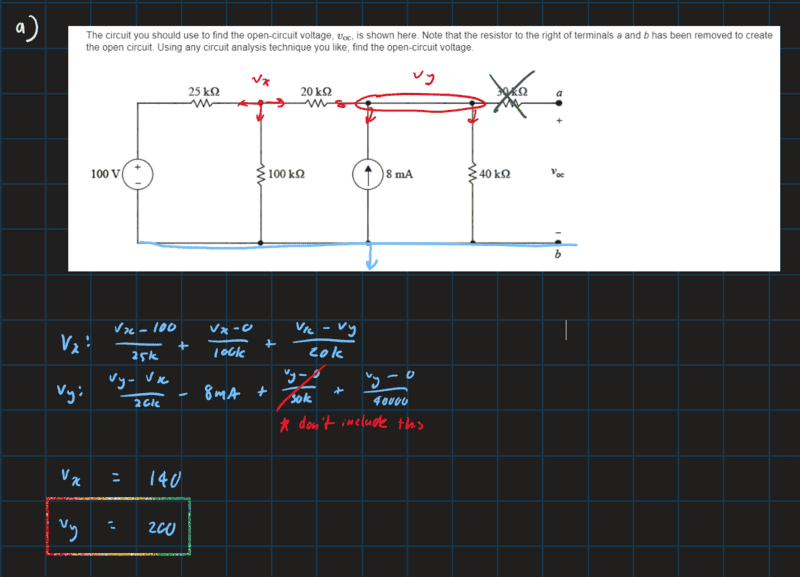
- The circuit you should use to find the open-circuit voltage, voc, is shown here. Note that the resistor to the right of terminals a and b has been removed to create the open circuit. Using any circuit analysis technique you like, find the open-circuit voltage.
- Relevant Equations
- KCL
I found how to get the solution to this question (the answer is 200V), but I don't understand why we ignore the 30kOhm resistor when using analysing the circuit. Because it is in series with the open voltage, wouldn't there be some voltage drop across the resistor that would affect the open-circuit voltage?
Thanks
Thanks