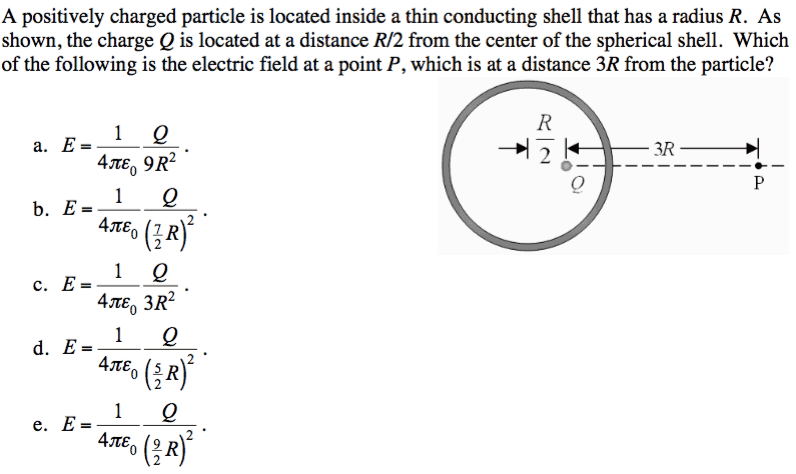Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around understanding the electric field near a conducting shell with a charge inside it. Participants are exploring the implications of the charge's position and the properties of conductors in electrostatics.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are questioning the significance of the charge being inside a conducting shell and its effect on the electric field. There are discussions about the application of Gauss's law and the uniformity of potential on the surface of the conductor.
Discussion Status
Some participants have offered insights into the relevance of Gauss's law and the concept of equipotential surfaces. There is an ongoing exploration of symmetry and boundary conditions in relation to the electric field configuration.
Contextual Notes
There appears to be some uncertainty regarding the radius mentioned in the problem and the assumptions about symmetry required for applying Gauss's law effectively.