- #1
moonrkr
- 2
- 0
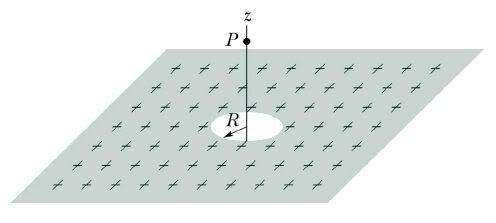
Electric Force problem --> Infinite charged plane with hole
The plane is infinite charged. It has a charge density (σ) of 10nC/m[itex]^{2}[/itex]. If R=5cm, determine the electric force of a proton in the point P=(0,0,10cm).
=====================================================================
MY set UP:
I was thinking about using E=σ/2*ε[itex]_{o}[/itex]
and use F=Eq.
I can see problems in the book with the infinite charged plane, but they don't have a hole thru it... PLEASE HELP>>>!
The plane is infinite charged. It has a charge density (σ) of 10nC/m[itex]^{2}[/itex]. If R=5cm, determine the electric force of a proton in the point P=(0,0,10cm).
=====================================================================
MY set UP:
I was thinking about using E=σ/2*ε[itex]_{o}[/itex]
and use F=Eq.
I can see problems in the book with the infinite charged plane, but they don't have a hole thru it... PLEASE HELP>>>!